
metastatic tumors is continuously evolving, with increasing
evidence supporting the benefit of controlling the primary
focus, notably for metastatic urothelial carcinoma of the
bladder
[4]. However, to date, there are no data available on
the role of radical nephrouretectomy (RNU) in the
treatment of mUTUC.
Thus, our objective was to test the impact of RNU on OS
in a select cohort of patients from the National Cancer Data
Base, who were deemed fit to receive systemic chemother-
apy for mUTUC. We hypothetized that for these individuals,
chemotherapy plus RNU is associated with an OS benefit
compared to chemotherapy alone.
From a population of 43 431 men and women diagnosed
with ureter or renal pelvis tumor between 2004 and 2012
(ICD-O-3 codes C65.9–C66.9), we identified 1182 individu-
als who received multiple-agent systemic chemotherapy
for unilateral mUTUC at presentation. Further exclusion
criteria are presented in Supplementary Fig. 1. Our final
study population included 1035 individuals, who were
dichotomized into a chemotherapy plus RNU group and a
chemotherapy-alone group.
To account for potential selection bias, observed
differences in baseline characteristics between patients
who received chemotherapy plus RNU and those who
received chemotherapy alone were controlled for with an
inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW)–adjust-
ed analysis
[5]. Balance in covariates between treatment
groups before and after IPTW adjustment was assessed
using the standardized difference approach. IPTW-adjusted
Kaplan-Meier curves and log-rank test were used to
compare OS between patients who received chemotherapy
plus RNU and those who received chemotherapy alone
[6]. In addition, we performed multivariable Cox regression
analysis to estimate the corresponding IPTW-adjusted
hazard ratio (HR)
[5].
Given the prognostic value of metastases locations for
mUTUC, we calculated separate IPTW-adjusted HRs for
chemotherapy plus RNU versus chemotherapy alone in
subgroups of patients with positive extraregional lymph
nodes only and bone/visceral involvement at initial
diagnosis by using interaction terms in the multivariable
Cox model. Finally, we assessed the impact of baseline
characteristics on the treatment effect by conducting a
locally weighted regression.
All statistical analyses were performed using SAS 9.4
(SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA). Two-sided statistical signifi-
cance was defined as
p
<
0.05. An institutional review board
waiver was obtained before the study was conducted.
Overall, 398 patients with mUTUC received chemothe-
rapy plus RNU (38.4%) and 637 (61.6%) received chemothe-
rapy alone (Supplementary Fig. 1). In the chemotherapy plus
RNU group, 357 (89.7%) and 41 (10.3%) patients received
surgery before and after chemotherapy, respectively.
Unweighted and weighted baseline characteristics of
eligible patients, stratified according to treatment group,
are reported in
Table 1 .Results of multivariable logistic
regression analysis predicting receipt of chemotherapy plus
RNU versus chemotherapy alone are reported in Supple-
mentary Table 1. Following IPTW adjustment, all standard-
ized differences were
<
10%, indicating that the treatment
groups were comparable (Supplementary Fig. 2).
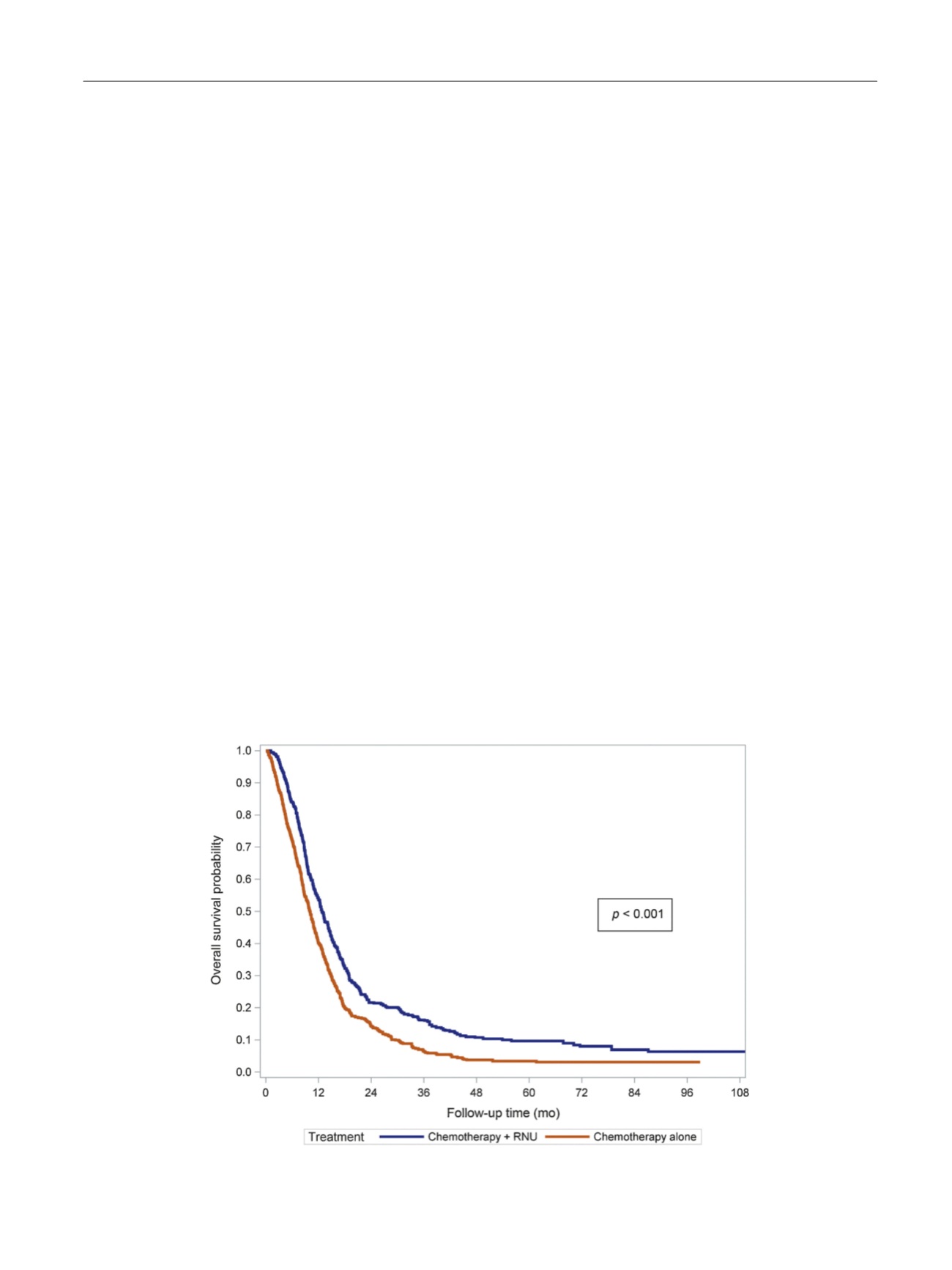
The median follow-up was 25.0 mo (interquartile range
11.4–52.2). IPTW-adjusted Kaplan-Meier curves
( Fig. 1)
showed that 3-yr OS was 16.2% (95% confidence interval
[CI] 12.1–20.3) for chemotherapy plus RNU and 6.4%
(95% CI 4.1–8.7) for chemotherapy alone (
p
<
0.001). In
[(Fig._1)TD$FIG]
Fig. 1 – Inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW)-adjusted Kaplan-Meier analysis of overall survival among patients who received
chemotherapy plus radical nephroureterectomy (RNU) versus chemotherapy alone for metastatic upper tract urothelial carcinoma.
E U R O P E A N U R O L O G Y 7 1 ( 2 0 1 7 ) 7 1 4 – 7 1 8
715
















